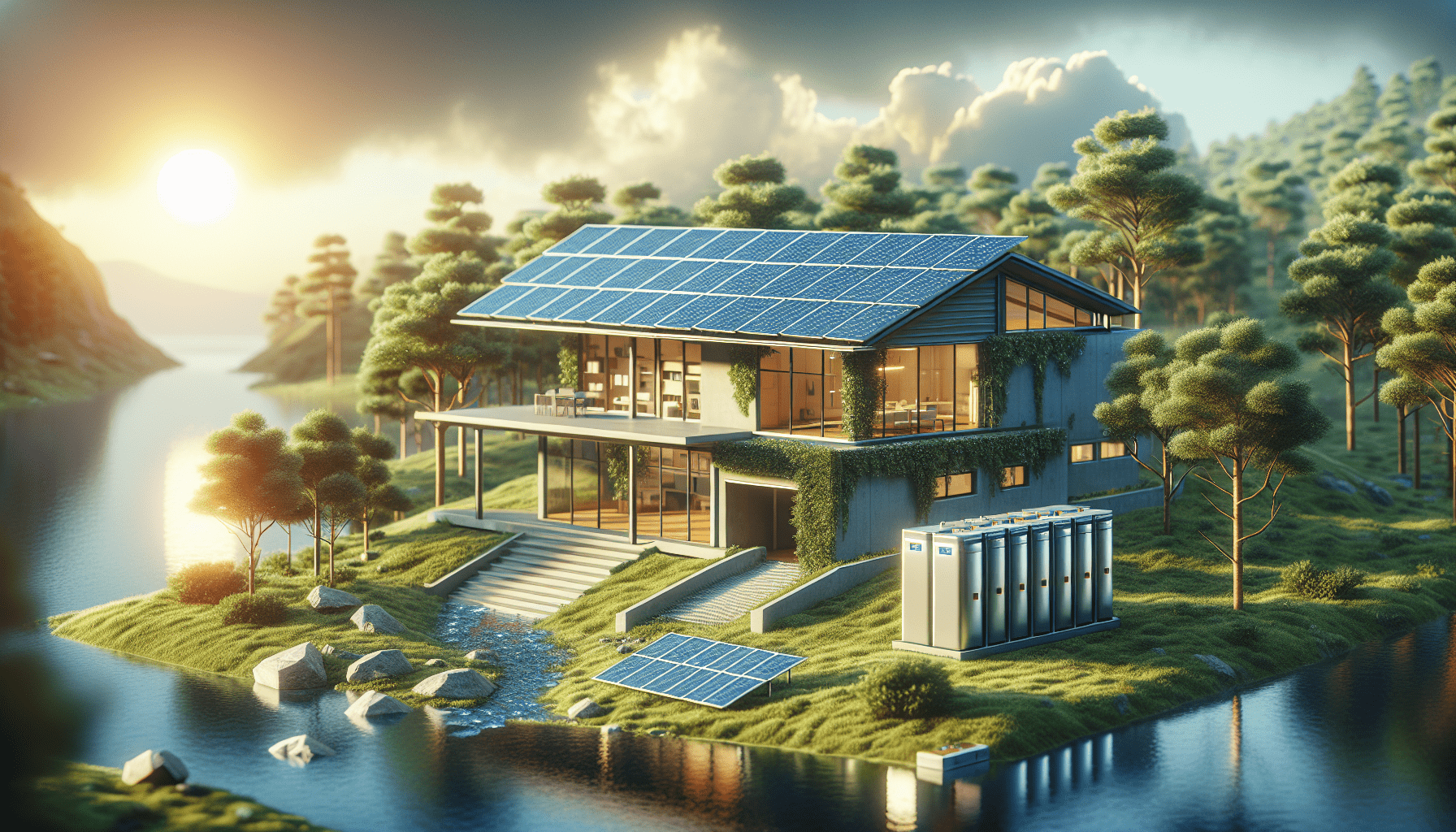
We have all heard the buzz about solar panels and their potential to reduce our carbon footprint and lower our electricity bills. But many of us may wonder, is it possible to go completely off-grid with solar panels? In other words, can we rely solely on solar power to meet all our energy needs without any connection to the traditional electric grid? The answer is yes, going off-grid with solar panels is indeed possible, and in this article, we will explore the benefits, challenges, and considerations of embracing a fully self-sustaining solar-powered lifestyle.

Understanding Off-Grid Solar Panels
Benefits of Going Off-Grid
Going off-grid with solar panels offers several exciting benefits. First and foremost, it allows us to become self-sufficient when it comes to energy. We are no longer reliant on the traditional power grid, which means we have greater control over our energy usage and costs. Additionally, going off-grid promotes sustainability and reduces our carbon footprint, as solar energy is a clean and renewable source of power. It also provides greater resilience in the face of power outages or natural disasters, ensuring that we still have access to electricity when the grid goes down.
How Off-Grid Solar Panels Work
Off-grid solar panels operate by converting sunlight into electricity through a process called photovoltaic (PV) effect. The panels are typically made up of silicon cells that contain layers of positively and negatively charged semiconductors. When sunlight hits the panels, the photons in the light excite the electrons in the semiconductors, causing them to create an electrical current. This direct current (DC) is then converted into alternating current (AC) through an inverter to power our household appliances.
Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar system consists of several key components that work together to harness and utilize solar energy efficiently. The main components include solar panels, a battery bank, an inverter, and charge controllers. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which is stored in the battery bank for later use. The inverter converts the DC power from the batteries into AC power for our everyday appliances, while the charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity between the panels, batteries, and appliances.
Assessing Your Off-Grid Solar Potential
Evaluating Your Energy Needs
Before embarking on an off-grid solar journey, it is crucial to evaluate our energy needs. By understanding our daily electricity consumption, we can determine the size of the solar system required to meet those needs. Consider the number and type of appliances we use regularly, as well as any special energy requirements such as heating or cooling systems. By assessing our energy needs accurately, we can ensure that our off-grid solar system is appropriately sized and capable of providing enough electricity for our daily activities.
Solar Resource Assessment
A solar resource assessment helps us determine the amount of sunlight available in our location. Factors such as latitude, climate conditions, and shading from trees or buildings can affect the solar potential of a site. It is advisable to consult resources like solar radiation maps or online calculators to estimate the average annual solar irradiation in our area. This assessment allows us to identify the optimal locations for solar panels, maximizing electricity generation.
Determining Panel Size and Battery Capacity
Based on our energy needs and solar resource assessment, we can calculate the appropriate panel size and battery capacity for our off-grid solar system. Panel size is determined by the wattage of each panel and the total power consumption. It is important to consider factors like the average daily sunlight hours and the efficiency of the panels. Battery capacity, on the other hand, is determined by the number of panels, the estimated daily energy consumption, and the desired autonomy level (number of consecutive cloudy days without sunlight). Properly sizing these components ensures that we have sufficient energy storage and power generation capabilities.
Choosing the Right Solar Panels
Types of Solar Panels
When it comes to off-grid solar panels, we have a variety of options to choose from. The most common types include monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar panels. Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency and sleek appearance. Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are more affordable but slightly less efficient. Thin-film solar panels are flexible and ideal for irregular surfaces. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, so it is essential to research and select the one that aligns best with our specific needs and budget.
Efficiency and Power Output
Efficiency and power output are crucial factors to consider when choosing solar panels for an off-grid system. Efficient panels convert a higher percentage of sunlight into usable electricity, maximizing energy production. Higher power output allows us to generate more electricity per panel, reducing the number of panels needed. It is important to find a balance between efficiency, power output, and cost to ensure that our off-grid solar system meets our energy requirements effectively.
Durability and Warranty
Durability is another important consideration when selecting solar panels. Off-grid systems are often exposed to harsh weather conditions, so it is essential to choose panels that can withstand extreme temperatures, strong winds, and hail. Look for panels with a high durability rating and a long warranty period to ensure they will last for many years. Investing in durable panels minimizes the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, maximizing the longevity and efficiency of our off-grid solar system.
Selecting a Suitable Battery System
Types of Batteries for Off-Grid Usage
Selecting the right batteries is crucial for storing and utilizing solar energy in an off-grid system. Common battery types for off-grid usage include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and saltwater batteries. Lead-acid batteries are affordable but require regular maintenance and have a relatively shorter lifespan. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are more expensive but offer higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and lower maintenance requirements. Saltwater batteries are a newer technology, environmentally friendly, and have a longer shelf life. Each type has its own benefits and considerations, so it is important to choose a battery system that aligns with our energy requirements and budget.
Sizing Your Battery Bank
Proper battery bank sizing is critical to ensure sufficient energy storage capacity for our off-grid solar system. The size of the battery bank depends on our daily energy consumption, desired autonomy level, and the type of batteries chosen. Calculating the battery capacity requires considering the depth of discharge (DOD), which determines the percentage of stored energy that can be utilized before recharging. A deeper DOD requires a larger battery bank size to prevent excessive discharge and potential damage to the batteries. By accurately sizing our battery bank, we can optimize the performance and longevity of our off-grid solar system.
Maintenance and Lifespan of Batteries
Regular maintenance is essential to prolong the lifespan and efficiency of off-grid solar batteries. This includes performing routine checks, cleaning terminals, and ensuring proper charging and discharging cycles. Some battery types require specific maintenance procedures, such as checking electrolyte levels in lead-acid batteries. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance and storage to avoid damaging the batteries. Additionally, monitoring the health of the batteries and replacing them when necessary will ensure that our off-grid solar system continues to function optimally.
Inverter and Charge Controller Considerations
Inverter’s Role in an Off-Grid System
The inverter plays a crucial role in converting the DC power stored in the batteries into AC power for our household appliances. In an off-grid system, the inverter must also have the capability to charge the battery bank using AC power when solar energy generation is insufficient. Some advanced inverters also have the ability to synchronize with backup generators, further enhancing the reliability and versatility of the off-grid system. It is important to select an inverter that matches the power capacity of our system and can handle the peak loads of our appliances.
Choosing the Right Inverter
When selecting an inverter for an off-grid system, several factors should be considered. These include the inverter type (pure sine wave vs. modified sine wave), the power rating, efficiency, and surge capacity. Pure sine wave inverters produce electricity that is similar to the power supplied by the traditional grid, ensuring compatibility with sensitive electronics and appliances. Modified sine wave inverters are more affordable but may not be suitable for certain devices. The power rating of the inverter should be sufficient to handle the peak loads of our appliances, while efficiency ensures optimal energy conversion. Surge capacity is important to handle the initial power surge when starting electrical motors or appliances.
Importance of Charge Controllers
Charge controllers are essential components of off-grid solar systems as they regulate the flow of electricity between the solar panels, battery bank, and appliances. They prevent overcharging of the batteries, which can damage them, and also protect against reverse current flow during nighttime or low sunlight conditions. Charge controllers come in different types, including PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking). PWM charge controllers are more affordable but less efficient, while MPPT charge controllers are higher in cost but offer increased power output and efficiency. Choosing a charge controller that matches our system’s voltage and amperage requirements is crucial to ensure optimal energy management.
Installation and Setup Process
Determining the Ideal Location
Choosing the ideal location for our solar panels is crucial to maximize sunlight exposure and energy generation. The panels should be installed in an area that receives ample sunlight throughout the day and is free of shade from trees or buildings. It is also important to consider the angle and tilt of the panels to optimize their performance in different seasons. Consulting solar resource maps or seeking professional advice can help determine the best location for solar panel installation.
Mounting the Solar Panels
Solar panels can be mounted on various structures such as rooftops, ground-mounted racks, or even pole-mounted structures. The choice depends on the available space, the orientation and tilt of the panels, and any local regulations or restrictions. It is important to ensure that the panels are securely mounted and positioned for maximum sunlight exposure. Mounting systems should be robust enough to withstand weather conditions and provide proper ventilation to prevent heat buildup.
Wiring and Connecting the Components
Wiring and connecting the components of an off-grid solar system should be done carefully to ensure safety and optimal performance. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and local electrical codes when wiring the solar panels, batteries, inverter, and charge controllers. Properly sizing the wires, using appropriate connectors, and creating a well-organized and labeled wiring system simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance tasks. For complex systems or if unfamiliar with electrical work, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a professional electrician to ensure a safe and reliable setup.

Load Management and Energy Efficiency
Prioritizing Essential Loads
In an off-grid solar system, it is important to prioritize essential loads to ensure that critical appliances have access to power even during periods of limited energy generation. Identifying which appliances are necessary for basic needs and assigning them to a dedicated circuit or load panel will enable us to manage our energy consumption effectively. By planning carefully and understanding our energy priorities, we can maximize the use of our solar energy and minimize the risk of running out of power.
Energy Conservation Techniques
Energy conservation is key in off-grid living to make the most of our limited energy resources. Implementing energy-efficient practices such as using LED lighting, turning off appliances when not in use, and optimizing heating and cooling systems can significantly reduce our electricity consumption. Insulating our homes, sealing drafts, and utilizing natural lighting can further enhance energy efficiency. By adopting these techniques and habits, we can ensure that our off-grid solar system meets our energy needs without straining the battery bank.
Monitoring and Managing Energy Usage
Regularly monitoring and managing our energy usage is essential to maintain a well-balanced off-grid solar system. A monitoring system can provide real-time information on energy production and consumption, helping us identify any energy inefficiencies or changes in patterns. By understanding our energy usage habits, we can make informed decisions and adjustments to optimize the performance of our off-grid system. Additionally, utilizing smart devices or timers can help automate certain tasks, such as turning on/off appliances during hours of peak solar energy production.
Backup Generators for Off-Grid Systems
The Role of Backup Generators
While solar panels provide reliable and clean energy, having a backup generator can provide an extra layer of security during prolonged periods of low sunlight or high energy demand. Backup generators can be used to charge the battery bank, power essential loads, or supplement the solar energy generation. It is important to select a generator that aligns with the power requirements of our off-grid system and consider factors such as fuel availability, noise level, and maintenance requirements.
Sizing and Fuel Considerations
When choosing a backup generator, proper sizing is crucial to ensure it can handle the peak loads and meet our energy needs effectively. Consider the power rating of the generator, estimated energy consumption, and the number of appliances that may need to be powered simultaneously. It is also important to consider the type of fuel the generator requires and its availability in our area. While diesel and gasoline generators are common options, there are also generators that run on propane or natural gas. Evaluating the availability, cost, and environmental impact of the fuel options is important when making a decision.
Integration with Solar Power System
To ensure seamless integration between the backup generator and the off-grid solar system, it is important to consider the wiring and control mechanisms. Automatic transfer switches or load management systems can automatically switch between solar power and generator power based on the available energy sources and load requirements. This integration guarantees uninterrupted power supply and prevents any potential conflicts between the solar system and the generator, optimizing the overall performance and efficiency of our off-grid system.
Managing and Troubleshooting Off-Grid Systems
Regular Maintenance Practices
Off-grid solar systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regularly cleaning the solar panels to remove dust, debris, or snow buildup is essential to maximize sunlight absorption. Checking the connections, wiring, and charge controllers to ensure they are secure and functioning properly is crucial. Monitoring the battery bank’s performance, checking charge levels, and inspecting for any signs of damage or deterioration is also important. By making maintenance practices a routine, we can prevent potential issues and prolong the lifespan of our off-grid solar system.
Dealing with Common Issues
Despite regular maintenance, off-grid systems may encounter common issues that require troubleshooting. Some common issues include insufficient energy generation, battery bank overcharging or undercharging, inverter failure, or damage to the solar panels. It is important to have a basic understanding of the system components and their functionality to diagnose and address these issues. Consulting the system’s manual, seeking guidance from professionals, or participating in online forums or communities can provide valuable insights and assistance when dealing with common off-grid system issues.
Professional Assistance
In some cases, seeking professional assistance may be necessary when managing and troubleshooting off-grid systems. Professional solar installers or electricians have the expertise and equipment to diagnose complex issues and provide effective solutions. They can also offer preventative maintenance services, periodic inspections, and system upgrades to ensure our off-grid solar system continues to operate at its best. When in doubt or when faced with technical challenges, it is advisable to reach out to professionals who specialize in off-grid solar installations.
Financial Considerations and Incentives
Cost of Going Off-Grid
Going off-grid with solar panels involves upfront costs for purchasing and installing the necessary components such as solar panels, batteries, inverters, and charge controllers. Additionally, there may be costs associated with system design, permits, and professional installation. It is important to budget for these expenses and consider the long-term financial benefits and energy savings that an off-grid solar system can provide. While the initial cost may seem significant, the potential for energy independence and reduced utility bills in the long run can make it a worthwhile investment.
Payback Period and Return on Investment
The payback period and return on investment for an off-grid solar system depend on various factors such as the initial cost, energy consumption, and utility rates. By comparing the costs of purchasing and installing an off-grid solar system with the projected energy savings over time, we can estimate the payback period. The return on investment is the duration it takes for the energy savings to surpass the initial investment. While the payback period may vary depending on individual circumstances, the long-term benefits of energy independence and reduced utility bills make off-grid solar a financially appealing option for many.
Government Support and Tax Incentives
In certain regions, governments provide support and tax incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable energy systems, including off-grid solar. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs and help offset the investment in an off-grid solar system. Tax credits, grants, and rebates are some common forms of government support available to homeowners or businesses transitioning to solar power. It is important to research and understand the available incentives in our region and take advantage of them to make the transition to off-grid solar more financially viable.
In conclusion, going off-grid with solar panels offers numerous benefits, from energy independence and sustainability to resilience and reduced carbon footprint. Understanding the components and functioning of an off-grid solar system is crucial to ensure its success. Assessing our energy needs, evaluating solar resources, choosing the right panels, batteries, inverters, and charge controllers, and following proper installation and maintenance practices are key steps in achieving an efficient off-grid system. By prioritizing essential loads, implementing energy conservation techniques, and considering backup generators when needed, we can effectively manage our energy usage. Regular monitoring, troubleshooting, and professional assistance ensure the continued smooth operation of our off-grid solar system. Financial considerations, including upfront costs, payback period, return on investment, and government incentives, should also be carefully evaluated to make informed decisions. With proper planning and a comprehensive understanding of off-grid solar systems, we can embark on an exciting journey towards energy independence and a greener future.