In our quest to make the most of natural resources, rainwater harvesting stands out as a smart and sustainable choice. Together, we can explore the best practices for collecting and utilizing this precious resource efficiently. From selecting the right catchment areas to employing proper filtration systems and storage solutions, this guide will walk us through essential steps to ensure that we capture, store, and use rainwater effectively. Let’s dive into the world of rainwater harvesting and discover how we can play our part in conserving water and nurturing our environment. Have you ever wondered how we can make the best use of rainwater? With the increasing scarcity of natural water sources, rainwater harvesting is becoming an essential practice worldwide. But what are the best practices for rainwater harvesting that can help us make the most out of every drop of rain that falls? Let’s dive into an in-depth exploration of effective rainwater harvesting techniques and guidelines.

Understanding Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting, storing, and using rainwater for various purposes like irrigation, household use, and even drinking water. By efficiently capturing rainwater, we can reduce dependency on traditional water supplies, lower our water bills, and contribute to sustainable water management.
Why Rainwater Harvesting is Important
Rainwater harvesting helps us ensure a sustainable water supply, especially in regions facing water shortages. It reduces the demand on rivers and groundwater, helps prevent urban flooding, and can even mitigate soil erosion. Plus, harvested rainwater is generally free from pollutants found in groundwater sources, making it an excellent alternative for various uses.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
There are several methods to harvest rainwater, each with its own set of practices and applications. Depending on our needs and the available space, we can choose from the following types:
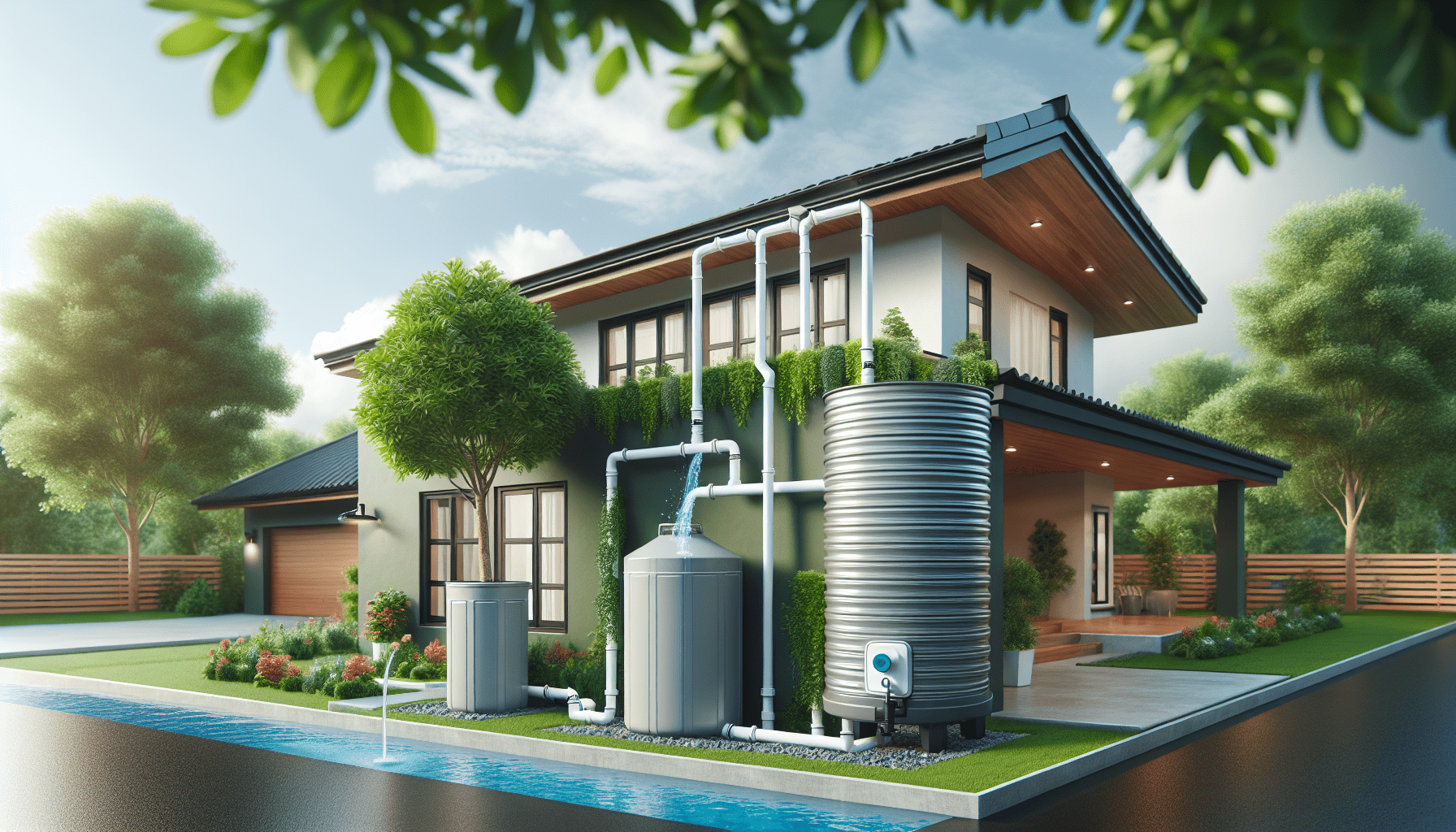
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
This method involves collecting rainwater that falls on the roof. It is one of the most common and efficient ways to harvest rainwater, especially in urban areas.
- Collection: Rainwater is collected from the roof using gutters.
- Conveyance: The collected water is conveyed through downspouts and pipes.
- Filtration: The water is filtered to remove contaminants.
- Storage: Finally, the water is stored in tanks or cisterns.
Surface Runoff Harvesting
Surface runoff harvesting captures rainwater that flows over land surfaces. This method is particularly useful in agricultural settings and areas with minimal infrastructure.
- Catchments: Constructed depressions or natural landscapes that collect runoff.
- Channels: Pathways that direct the runoff towards storage areas.
- Storage Ponds: Reservoirs where the runoff water is stored for future use.
Underground Rainwater Harvesting
This technique involves the collection of rainwater in underground tanks or through recharge of aquifers for long-term storage.
- Percolation Pits: Small, deep pits filled with porous materials.
- Recharge Wells: Wells that allow water to percolate and recharge underground aquifers.
- Underground Storage Tanks: Large tanks buried underground to store higher volumes of water.
Table of Different Rainwater Harvesting Systems
| Type | Method | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting | Roof Collection | Urban areas, Residential homes |
| Surface Runoff Harvesting | Catchments, Ponds | Agricultural fields, Rural areas |
| Underground Harvesting | Recharge Wells | Areas with declining groundwater |
Designing an Effective Rainwater Harvesting System
Designing a rainwater harvesting system requires careful planning to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. Here are the steps involved:
1. Assessing Water Needs and Availability
We need to evaluate our water needs and identify the amount of rainwater we can collect based on average rainfall and roof or catchment area size.
2. Choosing the Right Catchment Area
The surface where the rainwater will be collected is crucial. Roofs with non-toxic materials are ideal to ensure the harvested water is safe for use.
3. Installing Gutters and Downspouts
Gutters and downspouts are essential for directing the rainwater from the catchment area to the storage tanks. Proper installation ensures maximum water collection with minimum loss.
4. Filtering and Purification
Installing first-flush devices and filters to remove debris and contaminants ensures that the collected rainwater is clean and safe for various uses.
5. Storing Collected Water
Selecting the right storage tank based on capacity needs and space availability is vital. Tanks can be made from various materials such as plastic, concrete, or metal, depending on our preferences and budget.
6. Distribution System
A well-designed distribution system ensures that the stored water reaches the point of use efficiently. Using pumps and gravity-fed systems can help in effective water distribution.
Best Practices for Rainwater Harvesting
Following the best practices for rainwater harvesting can enhance system efficiency, ensure water quality, and extend the lifespan of the system. Here are some key practices we should follow:
Regular Maintenance
Regularly inspect and clean gutters, downspouts, filters, and storage tanks to prevent clogging and contamination.
Use of Sustainable Materials
Opt for sustainable and non-toxic materials for the catchment area, storage tanks, and conveyance system to ensure the safety and longevity of the system.
Water Quality Testing
Conduct periodic water quality testing, especially if the water is used for drinking or cooking, to ensure its safety.
Leak Prevention
Ensure that all connections, pipes, and tanks are well-sealed to prevent leaks and water wastage.
Proper Sizing
Size the system components appropriately based on the volume of rainwater expected and water needs. An oversized or undersized system can lead to inefficiencies.
Safety Measures
Install safety features such as overflow pipes, screen covers for tanks, and secure lids to prevent accidents and contamination by pests.
Community Engagement
Engage with the local community to share practices, joint initiatives, and education on the importance and benefits of rainwater harvesting.

Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Embracing rainwater harvesting can bring numerous environmental, economic, and societal benefits.
Environmental Benefits
- Reduces Flooding and Erosion: By capturing runoff, we can minimize urban flooding and soil erosion.
- Conserves Groundwater: Reduces extraction pressure on groundwater sources.
- Enhances Green Spaces: Provides a sustainable water source for irrigation in urban green spaces and agricultural fields.
Economic Benefits
- Cost Savings: Reduces water bills and reliance on external water sources.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Once installed, rainwater harvesting systems typically require minimal maintenance cost.
- Boosts Local Agriculture: Provides a stable water supply for irrigation, especially in drought-prone areas.
Societal Benefits
- Water Security: Ensures an additional water source during water scarcity or supply disruptions.
- Promotes Self-sufficiency: Empowers communities and households to become more independent regarding water supply.
- Educational Opportunities: Promotes awareness and education about water conservation and sustainable practices.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Rainwater Harvesting
While rainwater harvesting offers myriad benefits, it also comes with certain challenges. Understanding these challenges and implementing viable solutions can help us make the most of our rainwater harvesting systems.
Contamination Risk
Collected rainwater can be contaminated by debris, animal droppings, and chemicals from roofing materials.
Solution: Use first-flush diverters to prevent the initial flow of contaminants from entering the storage tanks. Regularly clean the catchment areas and install high-quality filters.
Limited Rainfall
In regions with inadequate or irregular rainfall, it might be difficult to collect sufficient rainwater.
Solution: Increase storage capacity to capture maximum rain during rainy periods. Implement supplementary water-saving practices to reduce overall water demand.
Initial Costs
The initial setup cost of rainwater harvesting systems can be a deterrent.
Solution: Consider the long-term savings and benefits. Seek out grants, subsidies, and community programs to offset some initial costs.
Space Constraints
Limited space in urban settings can pose a challenge to installing large storage tanks.
Solution: Utilize modular and compact storage options. Consider underground tanks or integrate the system with existing structures.

Case Studies of Successful Rainwater Harvesting
Examining successful rainwater harvesting initiatives can provide valuable insights and inspirations for our own projects.
Case Study 1: Chennai, India
Chennai, a coastal city in India, implemented widespread rooftop rainwater harvesting following a severe water crisis. The government mandated the installation of rainwater harvesting systems in all buildings, which resulted in a significant recharge of groundwater levels and improved water security for residents.
Case Study 2: Barcelona, Spain
The city of Barcelona introduced a comprehensive rainwater harvesting initiative to support its urban greening projects. Rainwater is collected from various municipal buildings and public spaces and used to irrigate parks and gardens, reducing the city’s dependence on potable water supplies and encouraging sustainable urban development.
How to Get Started with Rainwater Harvesting
If we’re inspired to start our own rainwater harvesting project, here’s a step-by-step guide to get us started.
Step 1: Education and Planning
Begin by educating ourselves about the various components and types of rainwater harvesting systems. Determine our water needs and plan the system accordingly.
Step 2: Site Assessment
Evaluate the available space, roof size, and other catchment areas. Assess the average rainfall in our region to estimate potential water collection.
Step 3: System Design
Design the system, including the collection, conveyance, filtration, and storage components. Consider consulting with experts to ensure the system is efficient and meets our needs.
Step 4: Installation
Purchase the required materials and install the system, following the design plan. Ensure all components are properly connected and secured.
Step 5: Maintenance and Monitoring
Regularly maintain the system by cleaning and inspecting all components. Monitor water quality and storage levels to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is not just a smart choice; it’s an essential practice in our era of water scarcity and environmental concerns. By implementing the best practices for rainwater harvesting, we can enjoy myriad benefits while contributing to a sustainable future. Whether we’re using the water for gardening, household needs, or replenishing groundwater, every drop counts. Let’s embrace rainwater harvesting and make a positive impact on our environment and community.



