How can we make a really impactful change on our environment? Let’s consider green energy and its pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions. Efforts to mitigate climate change have brought green energy to the forefront, prompting widespread adoption and innovation in renewable energy sources. In this article, we’ll explore how green energy works, its benefits, and how it helps in the fight against carbon emissions.
Understanding Green Energy
Green energy refers to the energy produced from natural resources like sunlight, wind, rain, tides, plants, algae, and geothermal heat. These energy sources are renewable, meaning they can be naturally replenished.
Types of Green Energy
Several forms of green energy are available today, each contributing in unique ways to reducing carbon emissions. Let’s explore some of these forms:
- Solar Energy: Captured from sunlight using photovoltaic cells or solar power plants.
- Wind Energy: Generated using wind turbines that convert wind energy into electricity.
- Hydropower: Produced by harnessing the energy from flowing water, typically using dams.
- Biomass Energy: Derived from organic materials like plant and animal waste.
- Geothermal Energy: Extracted from the heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface.
Renewable vs. Non-renewable Energy
Understanding the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy is essential in highlighting green energy’s benefits.
| Renewable Energy | Non-renewable Energy |
|---|---|
| Comes from sources that are naturally replenished. | Derived from finite sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas. |
| Includes solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal. | Primarily includes fossil fuels. |
| Emits little to no greenhouse gases. | Emits significant amounts of carbon emissions. |
Green Energy’s Impact on Carbon Emissions
Green energy can significantly reduce carbon emissions, a primary driver of climate change. Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources can help decrease the carbon footprint.
Reduction in Greenhouse Gases
Green energy systems emit little to no greenhouse gases during operation. For instance, solar panels and wind turbines generate electricity without burning fuel and hence don’t produce carbon dioxide (CO2).
Lifecycle Emissions
While it’s true that some emissions occur during the manufacturing and installation of renewable energy systems, lifecycle emissions for green energy sources are still significantly lower than that of fossil fuels. Lifecycle emissions encompass all emissions associated with a product’s life, from production to decommissioning.
Land Use and Ecosystem Preservation
Another aspect of green energy’s impact is its potential to preserve natural ecosystems compared to extractive processes required for fossil fuels. For example, large-scale wind farms and solar parks have a relatively low ecological footprint.
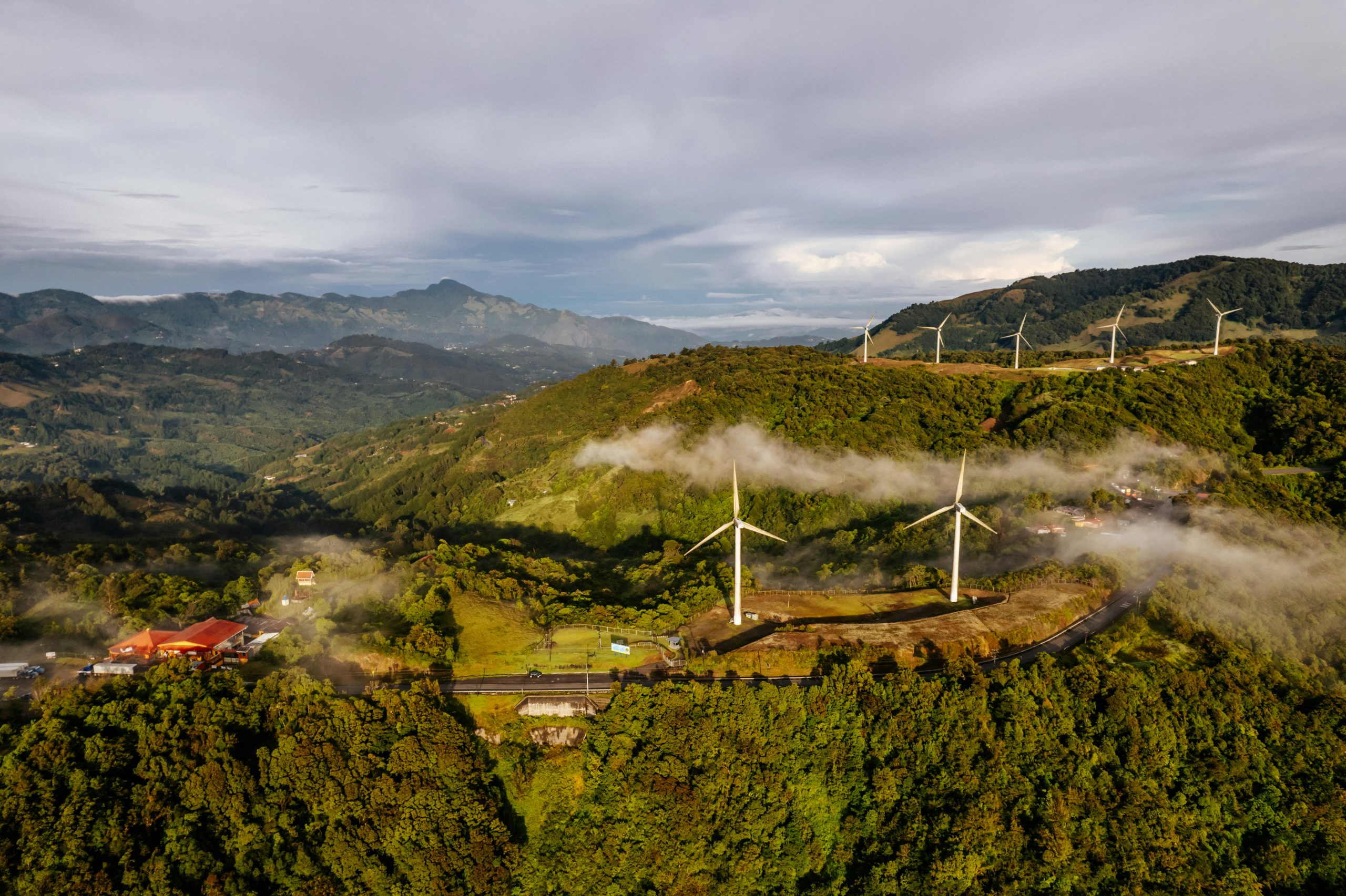

Benefits of Switching to Green Energy
Apart from the primary benefit of reducing carbon emissions, switching to green energy offers several other advantages.
Economic Advantages
Investing in green energy can stimulate economic growth. It creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of renewable energy facilities. Furthermore, it can reduce energy costs over the long term.
Security of Supply
Renewable energy sources are abundant and often local, which means reliance on imported fuels diminishes. This enhances energy security and stabilizes energy prices.
Public Health and Environment
Reducing air and water pollution associated with burning fossil fuels can lead to significant public health benefits. Better air quality can decrease health issues such as respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Overcoming Challenges
Transitioning to green energy is crucial, but it comes with challenges that need addressing to facilitate a smooth shift.
Technology and Infrastructure
We need advanced technology and infrastructure to support widespread adoption of green energy. For instance, efficient energy storage systems are required to manage intermittency issues with solar and wind power.
Investment and Policy Support
Sufficient investment and supportive policies are crucial in promoting green energy. Governments and private sectors need to collaborate to provide funding and incentives for renewable energy projects.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
Increasing public awareness and acceptance is vital. Community engagement and education can drive the transition to green energy by highlighting its benefits and the urgency of reducing carbon emissions.
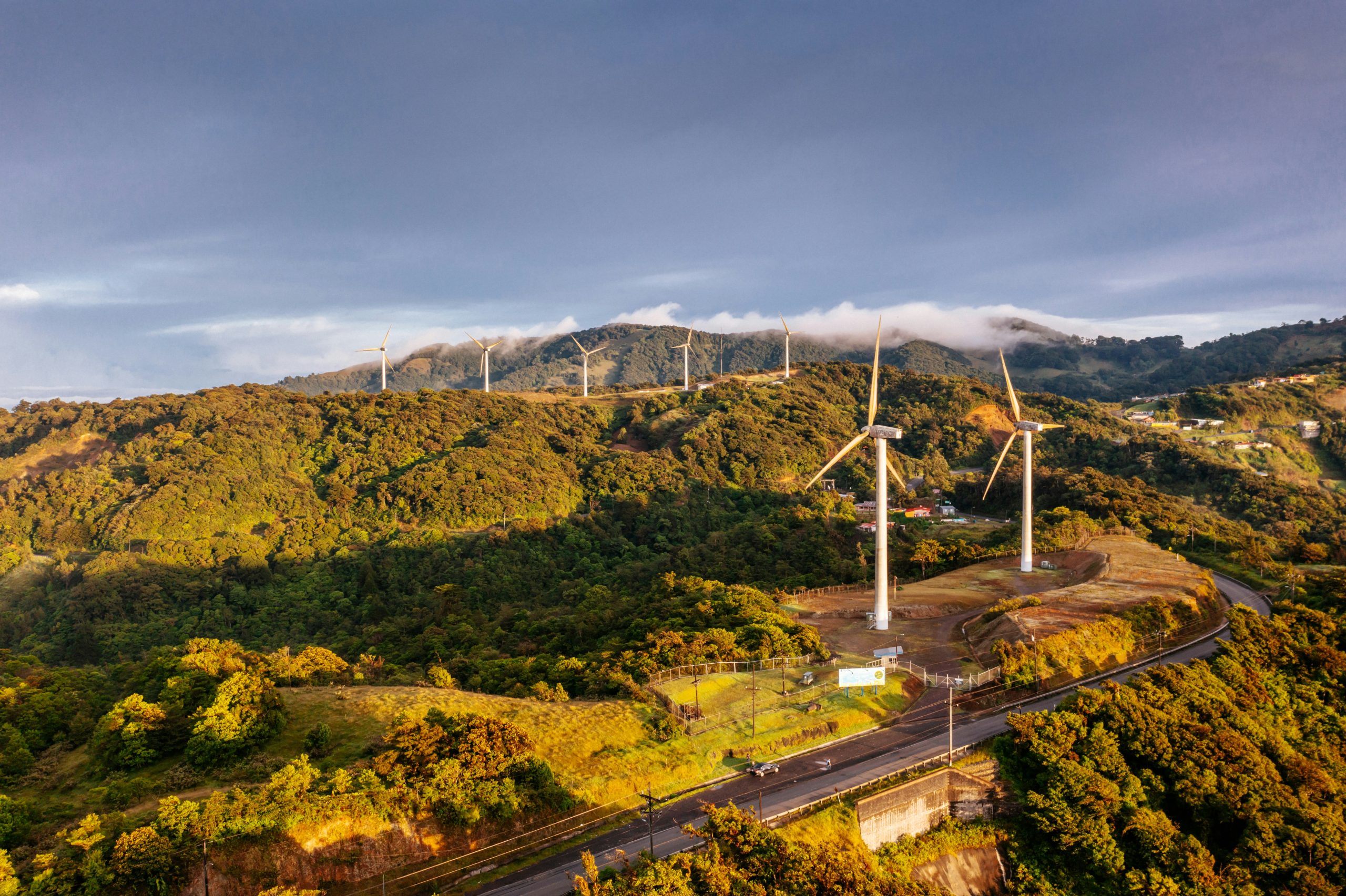

Case Studies of Green Energy Success
We can learn from various success stories around the globe where green energy projects have significantly reduced carbon emissions.
Germany’s Energiewende
Germany’s ambitious Energiewende, or “energy transition,” aims to shift to a renewable energy-dominated system. The country has made progress with policies supporting solar, wind, and biomass energy, significantly reducing its carbon emissions.
Costa Rica’s Renewable Energy Policy
Costa Rica has been a leader in renewable energy, regularly generating over 98% of its electricity from renewable sources like hydropower, wind, and geothermal energy. This has contributed to their remarkably low carbon footprint.
India’s Solar Energy Expansion
India has rapidly expanded its solar power capacity through initiatives like the Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission. This has not only alleviated electricity shortages but also reduced reliance on coal-based power.
Future Prospects of Green Energy
The future of green energy looks promising with continual advancements in technology and increased global commitment.
Innovations in Renewable Energy Technologies
Innovations in technologies like advanced wind turbines, more efficient photovoltaic cells, and enhanced geothermal systems are making green energy more viable and cost-effective.
Global Initiatives and Agreements
International agreements such as the Paris Agreement emphasize the importance of reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to renewable energy. Countries worldwide are setting ambitious targets for green energy adoption.
Personal and Community Initiatives
Personal choices, such as the adoption of solar panels on homes, and community-based renewable energy projects, are integral to the larger shift towards green energy. Local efforts can cumulatively make a substantial impact.

Conclusion
Understanding how green energy reduces carbon emissions involves looking at the various renewable energy sources, their benefits, and the challenges faced in transitioning from fossil fuels to a more sustainable future. By harnessing sources like solar, wind, and geothermal energy, we can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming.
It’s important to recognize the multiple benefits of green energy, including economic growth, energy security, and public health improvements. Furthermore, case studies around the world highlight the potential successes and lessons learned from countries leading the way in renewable energy adoption.
Addressing the challenges in this transition, such as technological development, investment needs, and public awareness, requires concerted efforts from governments, private sectors, and communities.
As we look ahead, continuous innovation in renewable energy technologies and the commitment to global initiatives will play crucial roles in ensuring a sustainable and environmentally friendly future for generations to come.